10.5 GRU
10.5.1 原理
GRU是LSTM的简化版本,仅有两个门控——重置门(遗忘)与更新门,同时也缺少记忆元,这使得GRU在训练时更加快捷。
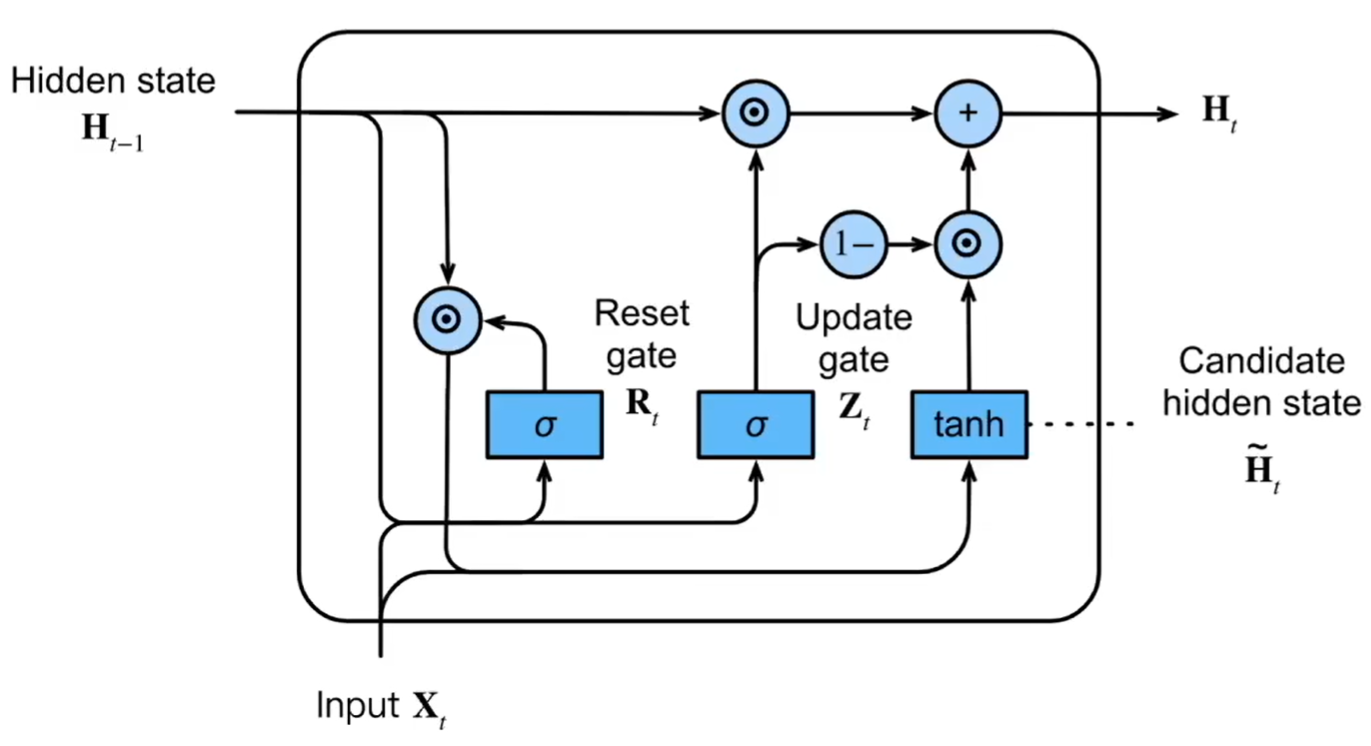
图 10.3: GRU
\[ \begin{aligned} R_t &= \sigma(X_t W_{xr} + H_{t-1} W_{hr} + b_r) \\ Z_t &= \sigma(X_t W_{xz} + H_{t-1} W_{hz} + b_z) \\ \tilde{H}_t &= \tanh(X_t W_{xh} + (R_t \odot H_{t-1}) W_{hh} + b_h) \\ H_t &= Z_t \odot H_{t-1} + (1 - Z_t) \odot \tilde{H}_t \end{aligned} \]
重置门\(R_t\)用于控制过去的隐藏状态有多少内容被用于生成当前候选隐藏状态,更新门\(Z_t\)用于控制生成当前隐藏状态时过去隐藏状态和候选隐藏状态的权重。
10.5.2 示例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ------------------------------
# 1. 生成模拟数据
# ------------------------------
# 我们造一个简单的任务:输入一个时间序列(正弦+噪声),预测最后一个时刻的值
np.random.seed(42)
torch.manual_seed(42)
def generate_data(num_samples=200, seq_len=20):
X = []
y = []
for _ in range(num_samples):
freq = np.random.uniform(0.5, 1.5)
phase = np.random.uniform(0, np.pi)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, seq_len)
seq = np.sin(np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi * freq, seq_len) + phase) + noise
X.append(seq)
y.append(seq[-1]) # 预测最后一个点
X = np.expand_dims(np.array(X), axis=2) # (N, T, 1)
y = np.expand_dims(np.array(y), axis=1) # (N, 1)
return torch.tensor(X, dtype=torch.float32), torch.tensor(y, dtype=torch.float32)
X, y = generate_data(num_samples=300, seq_len=30)
train_X, test_X = X[:240], X[240:]
train_y, test_y = y[:240], y[240:]
# ------------------------------
# 2. 定义 GRU 模型
# ------------------------------
class GRUNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size,
dropout=0.2, bidirectional=False):
super(GRUNet, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.bidirectional = bidirectional
self.gru = nn.GRU(
input_size=input_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
dropout=dropout if num_layers > 1 else 0.0,
bidirectional=bidirectional,
batch_first=True
)
# 如果是双向GRU,需要乘2
direction_factor = 2 if bidirectional else 1
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size * direction_factor, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
out, h = self.gru(x) # out: (batch, seq, hidden*direction)
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :]) # 取最后一个时间步的输出
return out
# ------------------------------
# 3. 初始化模型与优化器
# ------------------------------
model = GRUNet(
input_size=1, # 每个时间步输入1个特征
hidden_size=32, # 隐层维度
num_layers=1, # 堆叠1层GRU
output_size=1, # 输出一个数(预测值)
dropout=0.2,
bidirectional=False # 是否使用双向GRU
)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.005)
# ------------------------------
# 4. 训练模型
# ------------------------------
epochs = 100
train_losses = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(train_X)
loss = criterion(output, train_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_losses.append(loss.item())
if (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.6f}")
# 绘制训练损失曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(6,4))
plt.plot(train_losses)
plt.title("Training Loss Curve")
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("MSE Loss")
plt.show()
# ------------------------------
# 5. 测试与可视化
# ------------------------------
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(test_X).squeeze().numpy()
truth = test_y.squeeze().numpy()
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))
plt.plot(truth, label="True")
plt.plot(pred, label="Predicted")
plt.legend()
plt.title("GRU Prediction on Test Set")
plt.show()
# 计算误差指标
mse = np.mean((pred - truth)**2)
mae = np.mean(np.abs(pred - truth))
print(f"Test MSE: {mse:.6f}, MAE: {mae:.6f}")10.5.3 拓展
同LSTM。